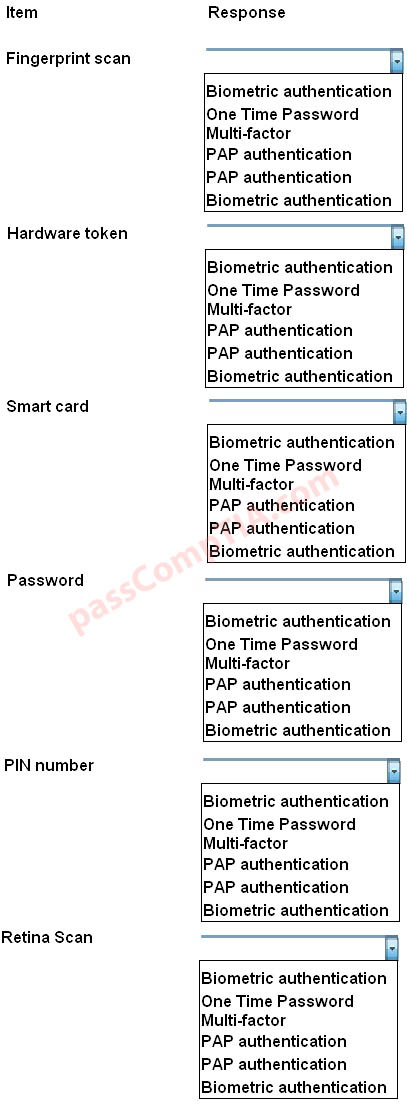
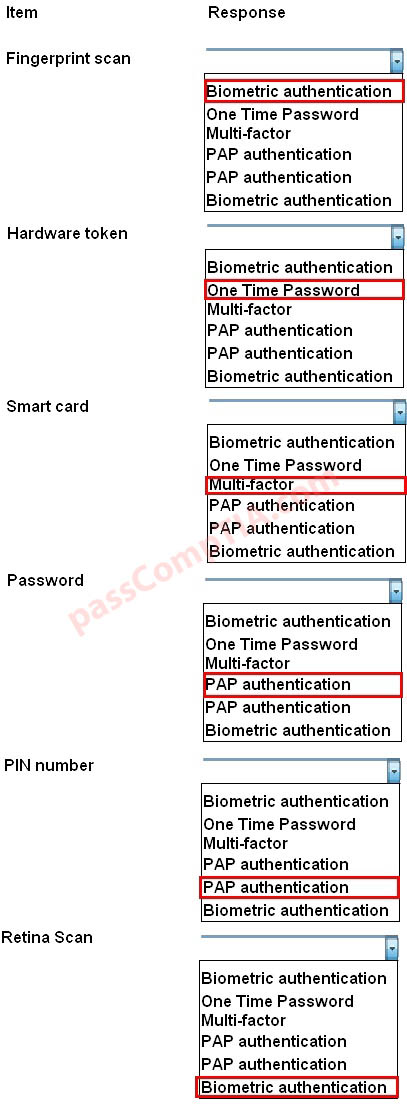
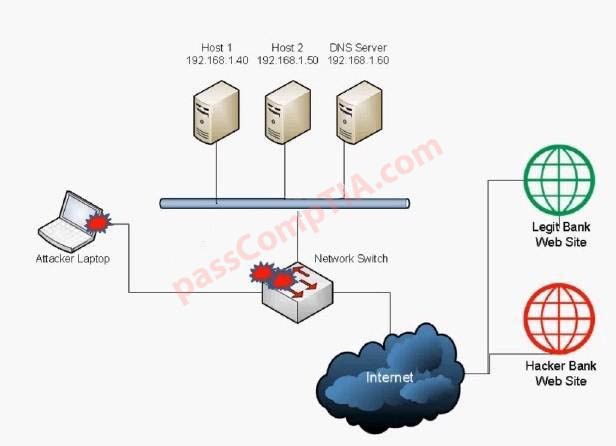
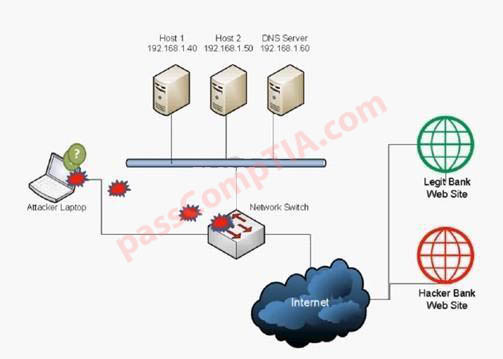
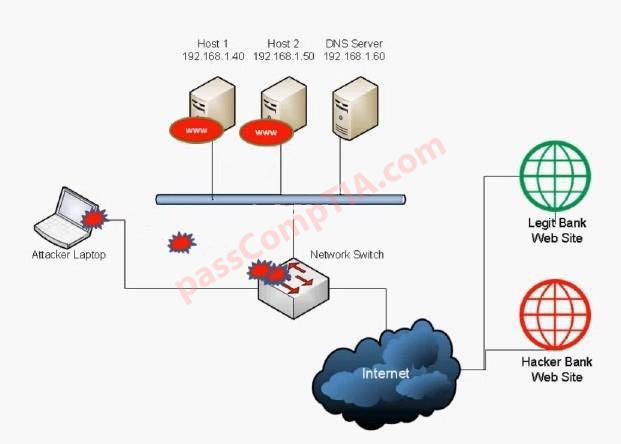
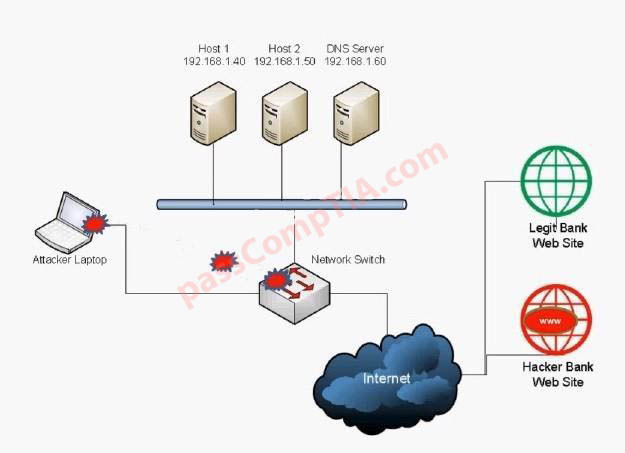
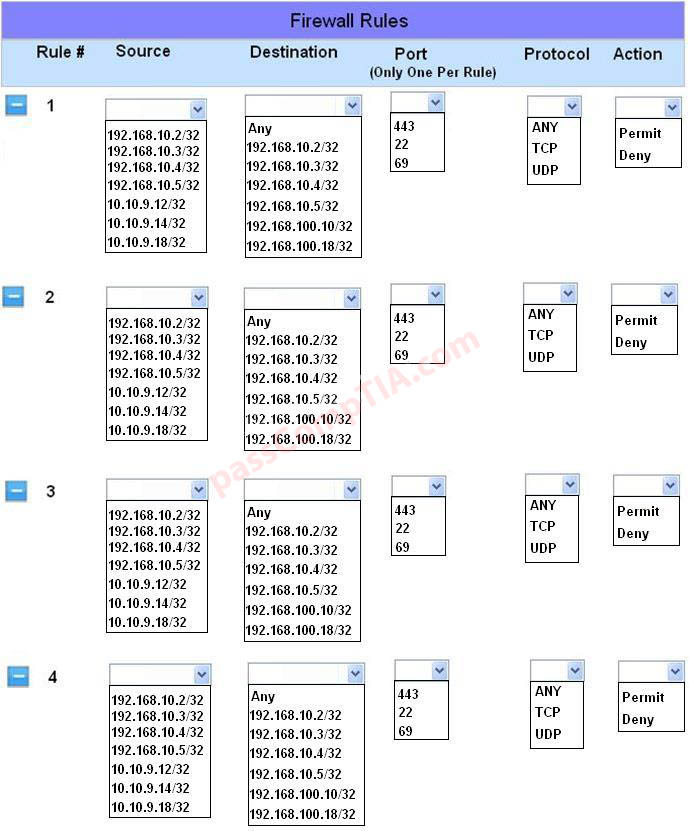
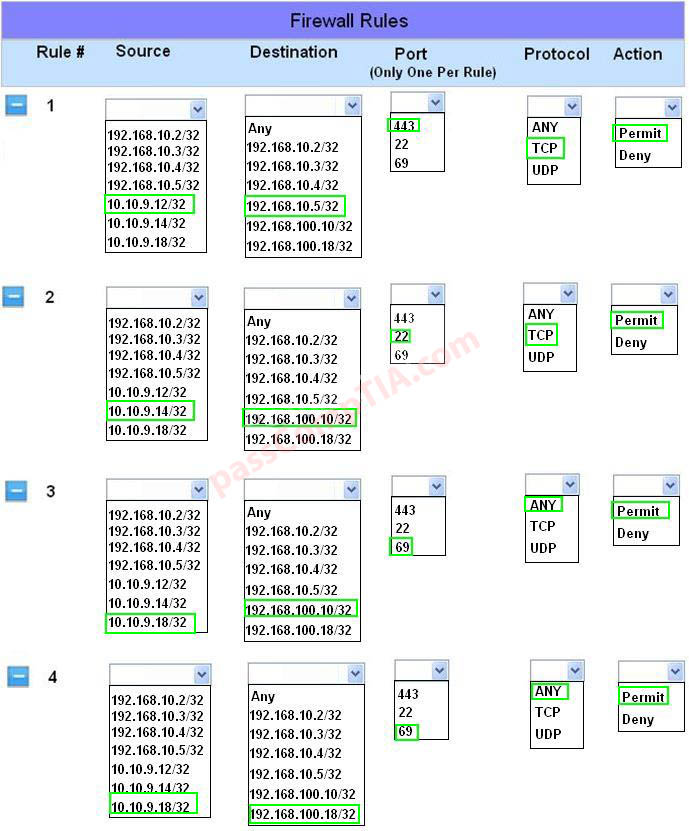
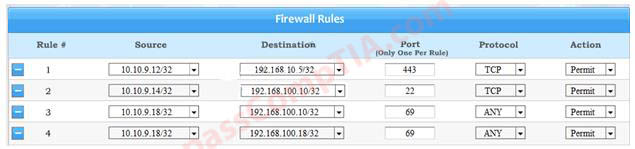
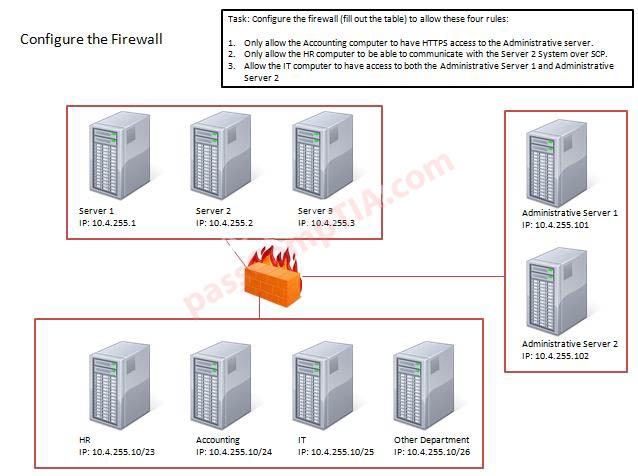
Configure the firewall to allow these four rules:
Use the following answer for this simulation task.
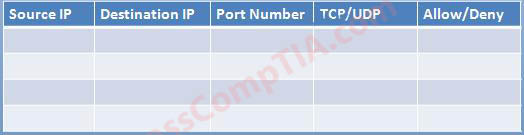
| Source IP | Destination IP | Port number | TCP/UDP | Allow/Deny |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10.4.255.10/24 | 10.4.255.101 | 443 | TCP | Allow |
| 10.4.255.10/23 | 10.4.255.2 | 22 | TCP | Allow |
| 10.4.255.10/25 | 10.4.255.101 | Any | Any | Allow |
| 10.4.255.10/25 | 10.4.255.102 | Any | Any | Allow |
Firewall rules act like ACLs, and they are used to dictate what traffic can pass between the firewall and the internal network. Three possible actions can be taken based on the rule’s criteria:
– Block the connection
– Allow the connection
– Allow the connection only if it is secured
TCP is responsible for providing a reliable, one-to-one, connection-oriented session. TCP establishes a connection and ensures that the other end receives any packets sent. Two hosts communicate packet results with each other. TCP also ensures that packets are decoded and sequenced properly. This connection is persistent during the session. When the session ends, the connection is torn down.
UDP provides an unreliable connectionless communication method between hosts. UDP is considered a best-effort protocol, but it’s considerably faster than TCP. The sessions don’t establish a synchronized session like the kind used in TCP, and UDP doesn’t guarantee error-free communications. The primary purpose of UDP is to send small packets of information. The application is responsible for acknowledging the correct reception of the data.
Port 22 is used by both SSH and SCP with UDP.
Port 443 is used for secure web connections – HTTPS and is a TCP port.
Thus to make sure only the Accounting computer has HTTPS access to the Administrative server you should use TCP port 443 and set the rule to allow communication between 10.4.255.10/24 (Accounting) and 10.4.255.101 (Administrative server1)
Thus to make sure that only the HR computer has access to Server2 over SCP you need use of TCP port 22 and set the rule to allow communication between 10.4.255.10/23 (HR) and 10.4.255.2 (server2)
Thus to make sure that the IT computer can access both the Administrative servers you need to use a port and accompanying port number and set the rule to allow communication between:
10.4.255.10.25 (IT computer) and 10.4.255.101 (Administrative server1)
10.4.255.10.25 (IT computer) and 10.4.255.102 (Administrative server2)
References:
Dulaney, Emmett and Chuck Eastton, CompTIA Security+ Study Guide, Sybex, Indianapolis