Which of the following provides the LEAST availability?
A. RAID 0
B. RAID 1
C. RAID 3
D. RAID 5
CompTIA exam questions
Which of the following provides the LEAST availability?
A. RAID 0
B. RAID 1
C. RAID 3
D. RAID 5
Establishing a published chart of roles, responsibilities, and chain of command to be used during a disaster is an example of which of the following?
A. Fault tolerance
B. Succession planning
C. Business continuity testing
D. Recovery point objectives
A software company has completed a security assessment. The assessment states that the company should implement fencing and lighting around the property. Additionally, the assessment states that production releases of their software should be digitally signed. Given the recommendations, the company was deficient in which of the following core security areas? (Select TWO).
A. Fault tolerance
B. Encryption
C. Availability
D. Integrity
E. Safety
F. Confidentiality
A small business needs to incorporate fault tolerance into their infrastructure to increase data availability. Which of the following options would be the BEST solution at a minimal cost?
A. Clustering
B. Mirrored server
C. RAID
D. Tape backup
Peter needs to track employees who log into a confidential database and edit files. In the past, critical files have been edited, and no one admits to making the edits. Which of the following does Peter need to implement in order to enforce accountability?
A. Non-repudiation
B. Fault tolerance
C. Hashing
D. Redundancy
Which of the following provides data the best fault tolerance at the LOWEST cost?
A. Load balancing
B. Clustering
C. Server virtualization
D. RAID 6
Matt, a security consultant, has been tasked with increasing server fault tolerance and has been given no budget to accomplish his task. Which of the following can Matt implement to ensure servers will withstand hardware failure?
A. Hardware load balancing
B. RAID
C. A cold site
D. A host standby
After recovering from a data breach in which customer data was lost, the legal team meets with the Chief Security Officer (CSO) to discuss ways to better protect the privacy of customer data.
Which of the following controls support this goal?
A. Contingency planning
B. Encryption and stronger access control
C. Hashing and non-repudiation
D. Redundancy and fault tolerance
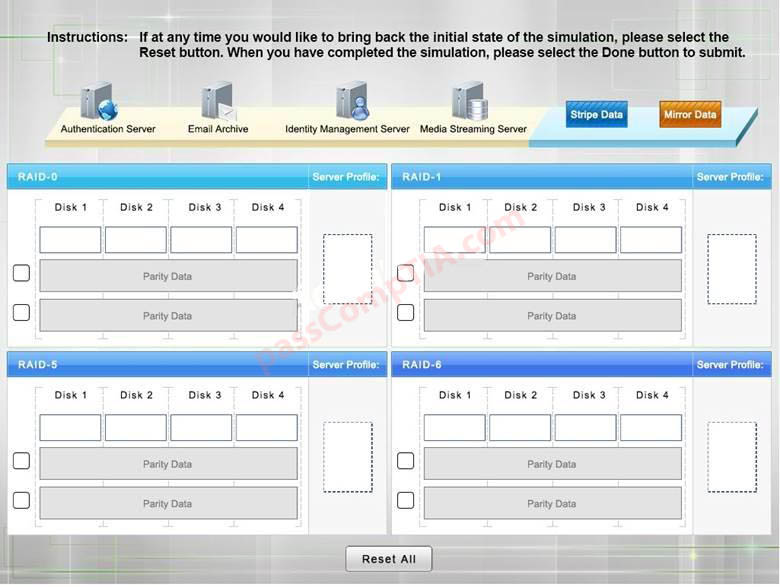
A security administrator is given the security and availability profiles for servers that are being deployed.
1) Match each RAID type with the correct configuration and MINIMUM number of drives.
2) Review the server profiles and match them with the appropriate RAID type based on integrity, availability, I/O, storage requirements.
Instructions:
• All drive definitions can be dragged as many times as necessary
• Not all placeholders may be filled in the RAID configuration boxes
• If parity is required, please select the appropriate number of parity check boxes
• Server profiles may be dragged only once
If at any time you would like to bring back the initial state of the simulation, please select the Reset
button. When you have completed the simulation, please select the Done