A security engineer must establish a method to assess compliance with company security policies as they apply to the unique configuration of individual endpoints, as well as to the shared configuration policies of common devices.
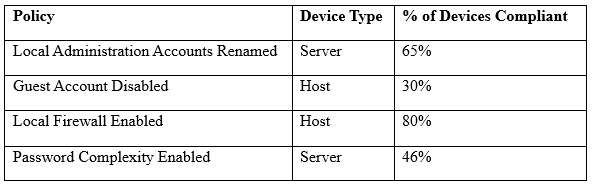
Which of the following tools is the security engineer using to produce the above output?
A. Vulnerability scanner
B. SIEM
C. Port scanner
D. SCAP scanner
CompTIA Security+ Question K-94
Which of the following tools would allow Ann, the security administrator, to be able to BEST quantify all traffic on her network?
A. Honeypot
B. Port scanner
C. Protocol analyzer
D. Vulnerability scanner
CompTIA Security+ Question J-72
Which of the following types of technologies is used by security and research personnel for identification and analysis of new security threats in a networked environment by using false data/hosts for information collection?
A. Honeynet
B. Vulnerability scanner
C. Port scanner
D. Protocol analyzer
CompTIA Security+ Question J-24
Which of the following should an administrator implement to research current attack methodologies?
A. Design reviews
B. Honeypot
C. Vulnerability scanner
D. Code reviews
CompTIA Security+ Question H-19
Peter a company’s new security specialist is assigned a role to conduct monthly vulnerability scans across the network. He notices that the scanner is returning a large amount of false positives or failed audits. Which of the following should Peter recommend to remediate these issues?
A. Ensure the vulnerability scanner is located in a segmented VLAN that has access to the company’s servers
B. Ensure the vulnerability scanner is configured to authenticate with a privileged account
C. Ensure the vulnerability scanner is attempting to exploit the weaknesses it discovers
D. Ensure the vulnerability scanner is conducting antivirus scanning
CompTIA Security+ Question G-62
Jane, a security analyst, is reviewing logs from hosts across the Internet which her company uses to gather data on new malware. Which of the following is being implemented by Jane’s company?
A. Vulnerability scanner
B. Honeynet
C. Protocol analyzer
D. Port scanner